-
Experiment 2 - A Flexible Diffraction Grating
PDMS may be cured in contact with the raised surface of a diffraction grating,
copying the surface features and making the polymer slab a flexible, transparent
diffraction grating. The polymer properties of this grating may be used in a
number of experiments.
Materials
- Flat, smooth glass or metal plate
- Convection oven capable of reaching 130º C
- Razor blade
- Square metal frame, such as a ~3 cm length of square pipe with sides of
~2.5 cm
- Sylgard Elastomer 184, obtained from Ellsworth
Adhesive Systems
- Pocket laser
- A disposable diffraction grating, such as # E39,502 from Edmund
Optics (the grating surface features are opposite the Edmund Scientific
logo) or an Optical Transform Slide from the Institute
for Chemical Education, or ICE, (the grating surface features are opposite
the "ICE" logo).
Figure 1. Disposable diffraction gratings from Edmund Scientific (top) and
The Institute for Chemical Education (bottom).
Procedure
- Place the grating, feature-side up, on the metal plate. Remove the frame
from the diffraction grating. Place the metal frame over the grating.
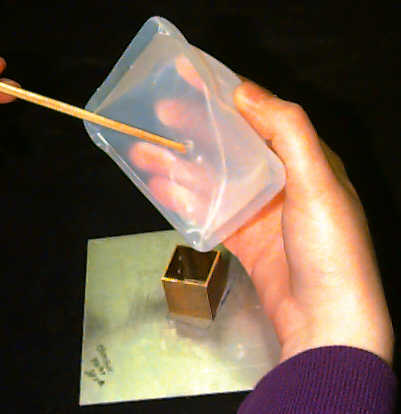

Figure 2. Recommended mold for making the flexible diffraction
grating.
- Prepare a ~3 g batch of PDMS; we recommend a ratio of curing agent to base
of between 1:10 and 1:15. After mixing the PDMS components thoroughly, set
the mixture aside for 15 minutes to allow bubbles to rise out of the PDMS.
Fill the diffraction slide/square frame assembly with PDMS and again set aside
for 15 minutes to allow bubbles to rise out of the PDMS.
- Place the asssembly into an oven at 130º C to cure the PDMS for 20
minutes. Remove the assembly and allow it to cool to room temperature. Carefully
remove the PDMS from its frame.
Explorations
- Place the PDMS diffraction slab in front of a laser beam (WARNING: Lasers
are high-intensity light sources; please follow recommended usage instructions)
with the beam entering from the side opposite the diffracting surface. The
laser beam diffracts.

Figure 3. Diffraction of a laser beam with the PDMS slab.
- Distorting the PDMS slab will distort the diffraction pattern. Shown below
is a square diffraction pattern generated by a square array of features on
the surface of a PDMS slab. Would you predict the diffraction pattern to stretch
or contract vertically as the slab itself is stretched vertically?
Figure 4. Distortion of a diffraction pattern by distortion of
the diffraction grating.
As the diffraction grating is stretched in a particular direction, the diffraction
pattern contracts in that same direction. This is referred to as the reciprocal
lattice effect and is a result of the wave nature of light.
Squeezing the diffraction slab fabricated above results in an increase in
spacing between the diffraction spots.

Figure 5. Squeezing a diffraction grating.
- Beside mechanical distortion, spacings between features on PDMS diffraction
gratings may be changed by other methods. PDMS has a high coefficient of thermal
expansion, so heating the grating (i.e. by heating it on a hot plate, for
a short time) will cause the diffraction pattern to contract as feature spacings
increase.

Figure 6. Heating a diffraction grating.
- PDMS may also be swelled as solvents such as toluene are absorbed by the
polymer. Solvent swelling of the grating will cause the diffraction pattern
to contract as feature spacings increase.

Figure 7. Solvent swelling a diffraction grating.
Return to the PDMS Main Page
Experiment 1 - The "Intial"
Stamp
Experiment 3 - Bouncing PDMS Balls
Experiment 4 - Surface Treatment of PDMS
Exploring
the Nanoworld |
MRSEC Nanostructured Interfaces
Copyright © 2006 The Board of Regents of the University
of Wisconsin System.