

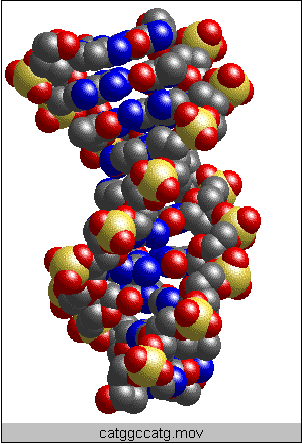
In this animation, a short space-filling model segment of B-DNA is rotating around its helical axis. This DNA segment has the well known double helical shape and contains 10 monomer units, or one full turn (or period) of the double helix. The phosphate groups (gold = P and red = O) lie along the outer edge of the molecule. The deoxyribose sugar units bonded to the phosphates appear mostly gray, because the carbon atoms, which comprise many of the atoms in sugars, are shown in gray, (the hydrogens are not shown). The base pairs that lie on the inside of the double helix, whose complementary hydrogen bonding holds the double helix together, look blue and gray (blue = N and gray = C). See if you can count the number of base pairs in the DNA segment.
As the animation proceeds, one strand of the double helix turns yellow, so you can more easily see each complementary strand of the DNA molecule.
Forward | [Introduction]